There are already more than 40 species of dolphins registered, belonging to various ecosystems and habitats, such as estuaries, rivers, coastal waters, and even the high seas, which, in itself, influences the diet of these beings.
In addition, food availability directly influences how they hunt. In this article, we will explain the types of food that some species of dolphins consume and the hunting methods they use.
What do dolphins eat?

These mammals, by nature, are active predators and usually have a very varied diet, consuming fish, squid, and crustaceans. There are 28 cetacean species present in the Azores region. Of these, 11 are dolphins, which, in itself, enhances the very similar diet they share.
With a wide distribution, the common dolphin is a species that relies on small schools of sardines and mackerel, but can also feed on squid and crustaceans.
Compared with other dolphins, bottlenose dolphins can feed on a wider variety of fish, including corvina, mackerel, and mullet, and also on cephalopods and crustaceans. Risso’s dolphins feed on deep-water animals such as squid, octopus, and cuttlefish.

As regards the diet of false killer whales, it is known to consist of large fish such as salmon, albacore, and tuna. Additionally, they consume squid, and they can still attack and eat other cetaceans.
Last but not least, we have the orcas! Known as formidable predators, this species of dolphin has a highly diverse diet, feeding on up to 150 species, including cetaceans, bony fish, sharks and rays, seabirds, and turtles.
✨ Related articles: Are Dolphins Endangered? | Are Pink Dolphins real? | Do Dolphins Eat Tuna? | Do Dolphins Smell? | Do Whales & Dolphins Lay Eggs?
Dolphin Hunting Methods
Dolphins can use a wide variety of hunting techniques, which depend on the type of prey in sight and its location.
Fish Whacking
One of the techniques that dolphins use is “Fish Whacking”, which involves stunning the fish with a blow from the tail, sometimes throwing the fish out of the water and catching it.
Strand Feeding
We also have strand feeding when dolphins create waves to push fish to the edge of the mud. When trapped, dolphins move to the shore temporarily to catch fish. This technique occurs mainly in rivers and estuaries.
Mud Ringing
Finally, we have “Mud Ringing”, in which a dolphin creates a ring-shaped mud plume that forms a turbidity barrier around the fish. These, when trying to escape through the surface of the water, are caught in the air by the remaining dolphins of the group.
Beaching
Orcas also employ a wide range of feeding strategies. One of these strategies is the beaching method of ambushing prey (mostly seals), driving them ashore, and then capturing them.
Wave washing
In addition to the strategy described above, orcas also use the technique of “wave washing” to dislodge seals from the ice blocks they rest on. To succeed, they must work as a team, creating waves with their bodies to move the ice block, causing the seal to eventually fall into the water.
Carousel feeding
The carousel feeding technique consists of forming a group ball and then capturing the herring of the shoal.
How do dolphins find their prey?
Dolphins and other species use echolocation a lot to find their prey. This evolutionary adaptation enables dolphins to distinguish the size and type of fish.
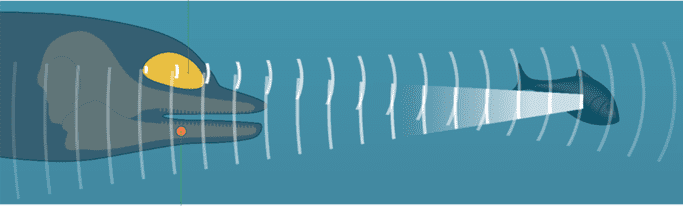
Echolocation is a biological process that involves the production of sounds by biosonars in the nasal passages, which are subsequently emitted through the melon (a structure at the front of the head, shown in yellow in the illustration). These sound waves bounce off targets and are reflected back to the emitting dolphin. The returning echoes are received in the lower jaw (orange sphere) and transmitted to the ear.

Conclusion
As previously mentioned, the Azores are home to a wide diversity of cetacean species. The presence of such a large number of species in this region leads to the formation of various feeding niches and, consequently, a high diversity of feeding techniques.
Considering that different cotypes of the same species may exhibit different feeding techniques depending on their habitat, visiting the Azores may offer a unique opportunity to observe such feeding behaviors. Come with Futurismo to explore the possibility of witnessing extraordinary behaviors!
References
- Berta, A. (Ed.). (2015). Whales, dolphins, and porpoises: A natural history and species guide. University of Chicago Press.
- Carwardine, M. (2019). Handbook of whales, dolphins, and porpoises. Bloomsbury Publishing.
















































